Home>Arts and Culture>The Significance Of The Byzantine Empire’s Creation Of The Basilica Of Hagia Sophia


Arts and Culture
The Significance Of The Byzantine Empire’s Creation Of The Basilica Of Hagia Sophia
Published: February 10, 2024
Jason DeRose, Managing Editor at Christian.net, uses his expertise in religion and journalism to deepen understanding of faith's societal impacts. His editorial leadership, coupled with a strong academic background, enriches the platform’s diverse content, earning him recognition in both journalism and religious circles.
Explore the historical and cultural significance of the Byzantine Empire's creation of the Basilica of Hagia Sophia, a masterpiece of arts and culture that continues to inspire awe and admiration. Discover the architectural marvel that stands as a testament to the empire's enduring legacy in arts and culture.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Christian.net, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
The Byzantine Empire, renowned for its rich cultural heritage and architectural marvels, left an indelible mark on history. One of its most iconic contributions to the world of architecture is the Basilica of Hagia Sophia. This majestic structure stands as a testament to the empire's grandeur and the ingenuity of its architects and artisans. The creation of Hagia Sophia marked a pivotal moment in the evolution of architectural design, setting new standards for grandeur and magnificence that continue to inspire awe and admiration to this day.
The significance of the Basilica of Hagia Sophia extends far beyond its physical presence. It embodies the fusion of diverse cultural influences, reflecting the empire's embrace of artistic and architectural elements from various civilizations. This amalgamation of styles and techniques resulted in a structure that transcends time, captivating the imagination of all who behold its splendor.
As we delve into the story of the Basilica of Hagia Sophia, we unravel the intricate tapestry of the Byzantine Empire's cultural and artistic prowess. From its construction to its enduring legacy, the journey of Hagia Sophia offers a profound insight into the empire's commitment to excellence and innovation. Join us as we embark on a captivating exploration of this architectural masterpiece and the profound impact it has had on the world of art and culture.
Read more: What Is The Significance Of Lent?
The Byzantine Empire's Influence on Architecture
The Byzantine Empire, spanning over a millennium, exerted a profound influence on the development of architectural styles and techniques. Its impact reverberated across continents, shaping the aesthetic sensibilities of diverse cultures and civilizations. At the heart of this influence was the empire's unique amalgamation of Eastern and Western architectural traditions, resulting in a distinctive and enduring legacy.
One of the defining characteristics of Byzantine architecture was its emphasis on grandeur and opulence. The empire's architects sought to create structures that embodied the majesty and splendor of the imperial court, utilizing intricate mosaics, ornate domes, and lavish ornamentation to achieve this effect. This penchant for grandiosity permeated the design of churches, palaces, and public buildings, leaving an indelible mark on the architectural landscape.
The Byzantine Empire's architectural innovations extended beyond mere aesthetics. The construction of monumental domes, such as those found in the Hagia Sophia and other Byzantine churches, showcased the empire's mastery of engineering and structural design. These awe-inspiring domes, often adorned with radiant mosaics depicting religious motifs, became emblematic of Byzantine architecture, symbolizing the empire's spiritual and artistic aspirations.
Furthermore, the empire's strategic location at the crossroads of Europe and Asia facilitated the exchange of architectural ideas and techniques. Byzantine architects drew inspiration from diverse sources, incorporating elements from Roman, Greek, Persian, and Syrian traditions into their designs. This synthesis of influences resulted in a fusion of styles characterized by intricate geometric patterns, elaborate arches, and the extensive use of marble and precious stones.
The enduring legacy of the Byzantine Empire's architectural influence is evident in the preservation of its iconic structures and the emulation of its design principles in subsequent eras. The grand domes, intricate mosaics, and ornate facades that define Byzantine architecture continue to captivate and inspire architects, artists, and admirers of cultural heritage worldwide.
In essence, the Byzantine Empire's influence on architecture transcends mere construction; it represents a convergence of artistic, cultural, and engineering achievements that have left an indelible imprint on the world's architectural heritage. The enduring allure of Byzantine architecture serves as a testament to the empire's enduring legacy and its enduring impact on the evolution of architectural expression.
The Creation of the Basilica of Hagia Sophia
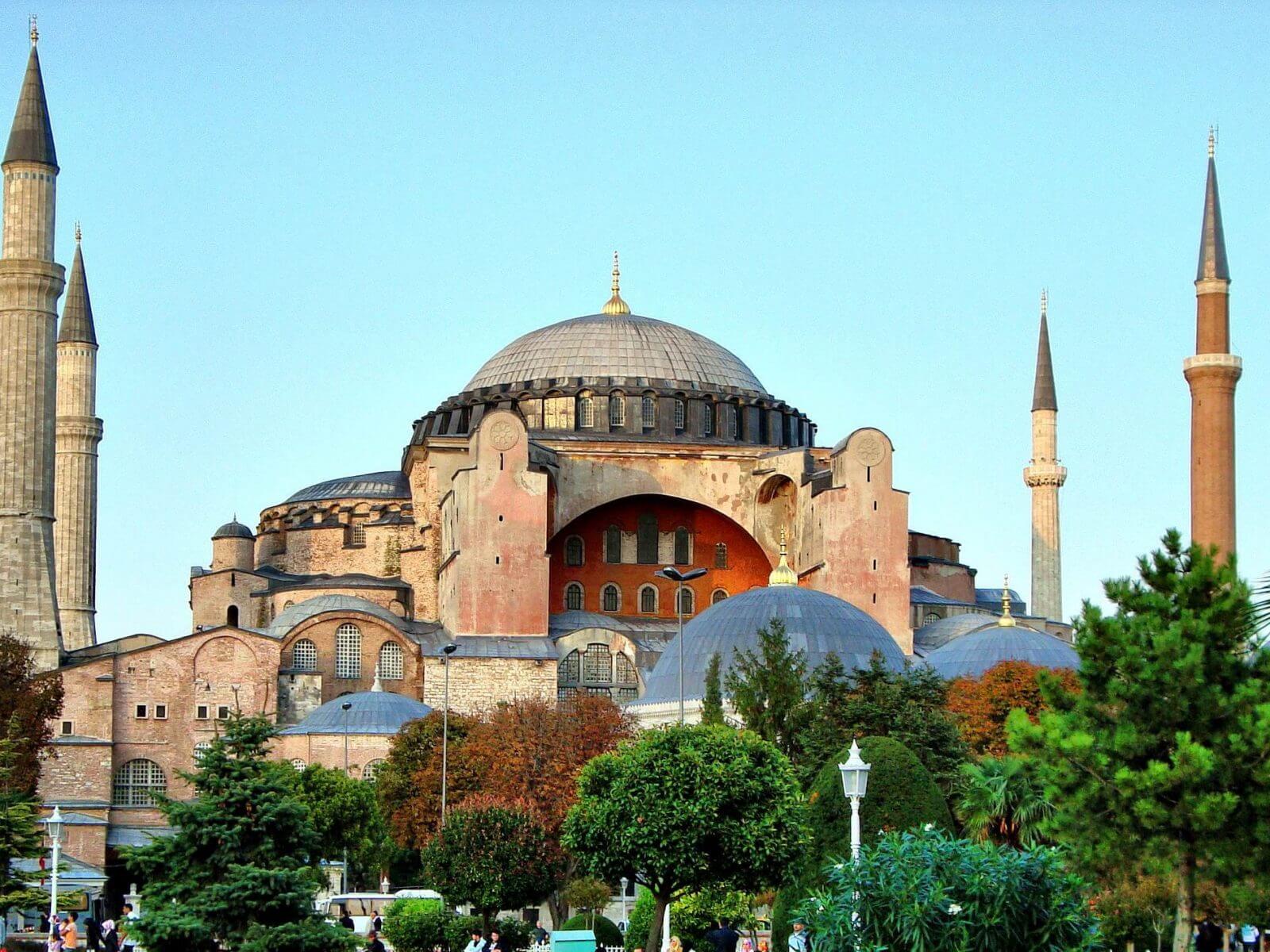
The creation of the Basilica of Hagia Sophia stands as a crowning achievement of the Byzantine Empire's architectural prowess. Commissioned by Emperor Justinian I and designed by the architects Isidore of Miletus and Anthemius of Tralles, the construction of Hagia Sophia commenced in 532 AD and was completed in a remarkably short span of five years. This ambitious undertaking aimed to surpass the grandeur of all existing churches and establish a monument that would symbolize the empire's power and divine favor.
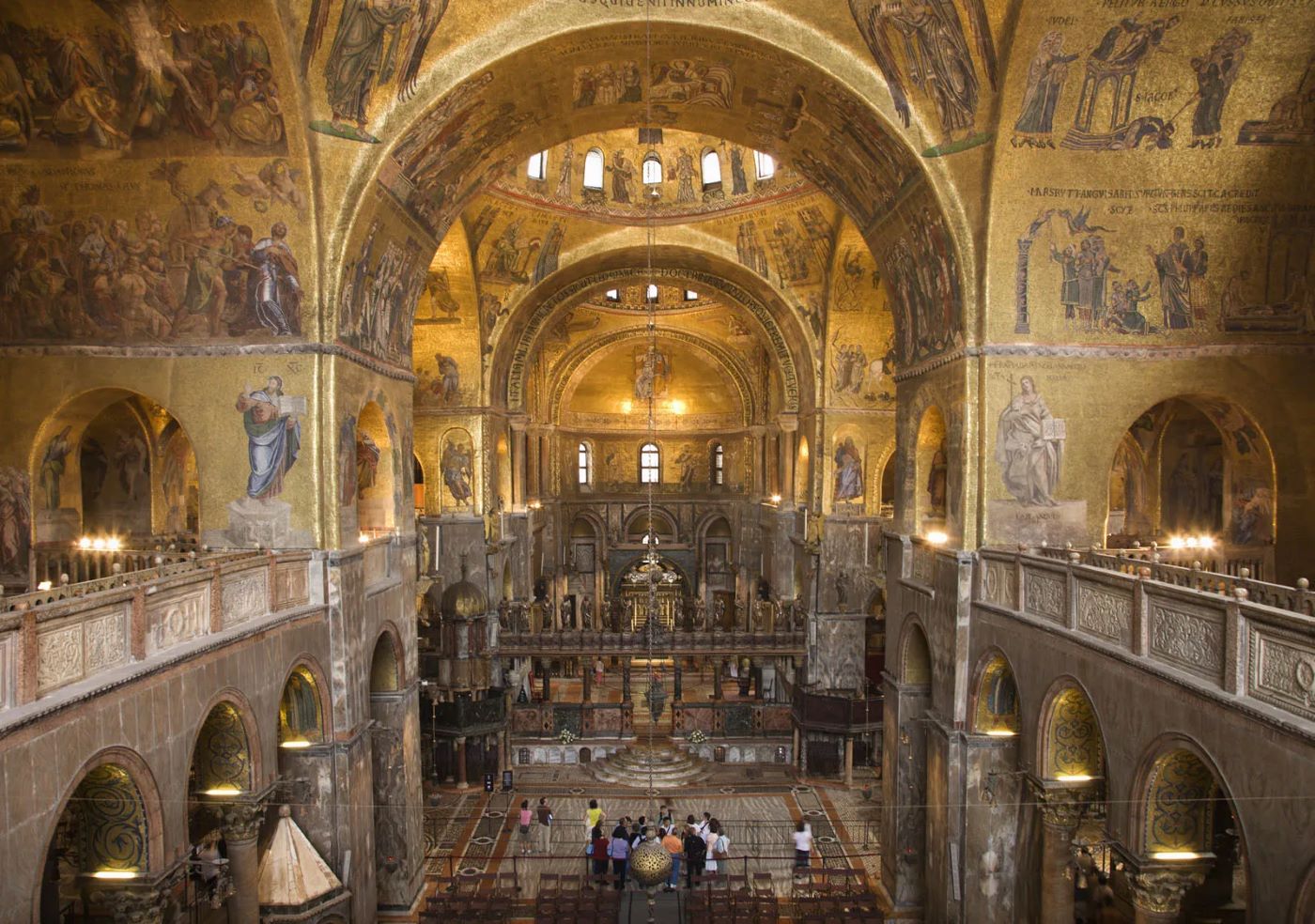
The architects' innovative approach to engineering and design resulted in a structure that defied the architectural conventions of its time. The most striking feature of Hagia Sophia is its massive dome, which, at the time of its construction, was the largest in the world. The dome's immense size and seemingly weightless appearance were achieved through the strategic use of pendentives, semi-domes, and carefully placed supporting structures. This architectural marvel not only showcased the empire's engineering ingenuity but also set a new standard for monumental domed structures.
The interior of Hagia Sophia is adorned with a breathtaking display of mosaics, marble columns, and intricate designs that reflect the empire's commitment to opulence and artistic excellence. The interplay of light and space within the vast interior creates an ethereal ambiance, evoking a sense of divine transcendence. The building's architectural elements, including the exquisitely carved capitals and the ornate decoration of the galleries, exemplify the empire's dedication to creating a space that embodied both earthly and celestial splendor.
The construction of Hagia Sophia represented a convergence of diverse cultural influences, incorporating elements from Roman, Greek, and Eastern traditions. This synthesis of styles resulted in a structure that transcended the boundaries of time and geography, embodying the empire's cosmopolitan ethos and its aspiration to create a monument that would stand as a testament to its cultural and religious preeminence.
Upon its completion, Hagia Sophia was consecrated as the patriarchal cathedral of Constantinople, serving as the spiritual heart of the Byzantine Empire. Its significance extended beyond religious worship, as it also served as a symbol of imperial power and a testament to the empire's commitment to architectural innovation. The creation of Hagia Sophia marked a defining moment in the history of architecture, setting a new standard for monumental construction and leaving an indelible imprint on the cultural landscape of the Byzantine Empire.
The Basilica of Hagia Sophia stands as a testament to the Byzantine Empire's architectural and artistic achievements, embodying the empire's grandeur and cultural sophistication. Its creation represents a triumph of human ingenuity and a lasting legacy of the empire's enduring impact on the world of architecture.
The Significance of Hagia Sophia in Byzantine Culture
The Basilica of Hagia Sophia holds profound significance in the cultural tapestry of the Byzantine Empire, transcending its role as a mere architectural marvel. It served as a focal point for the empire's religious, political, and artistic endeavors, embodying the essence of Byzantine culture in its most sublime form.
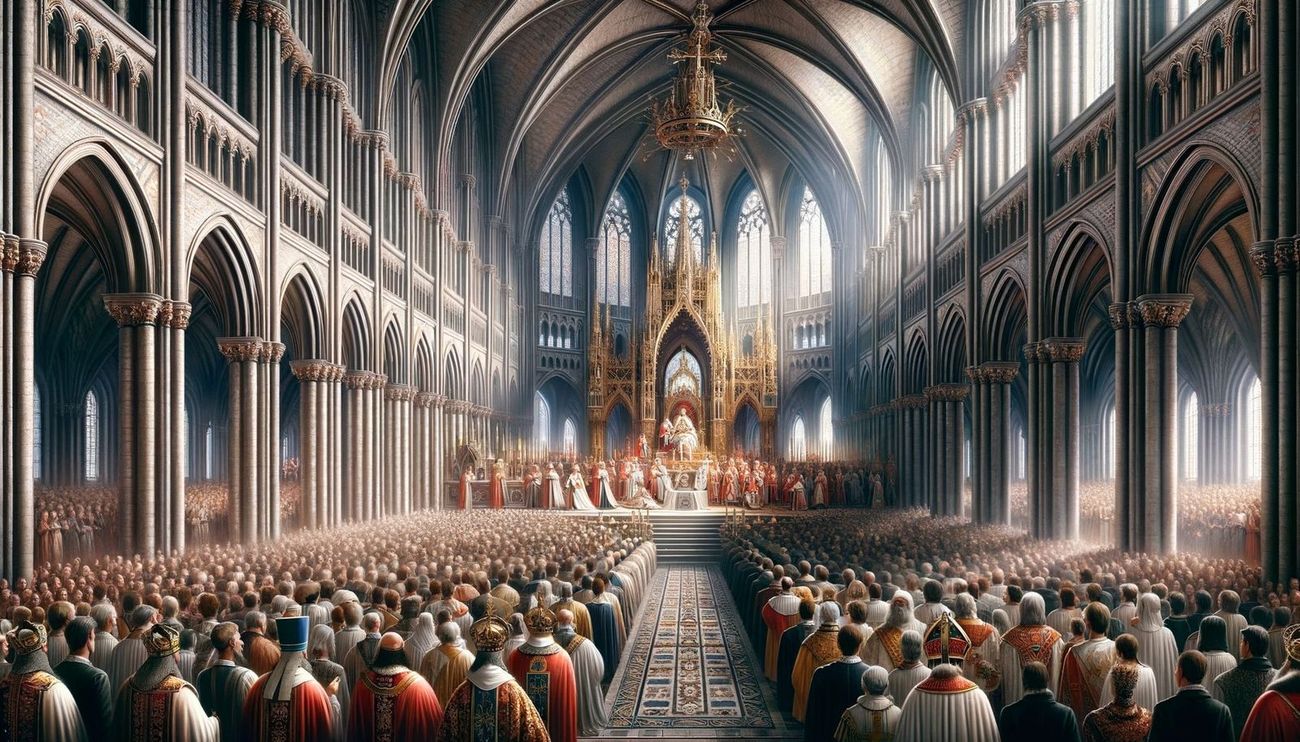
As the patriarchal cathedral of Constantinople, Hagia Sophia stood as a testament to the empire's unwavering commitment to Christianity. Its imposing presence and resplendent interior conveyed a sense of divine grandeur, serving as a physical manifestation of the empire's spiritual aspirations. The intricate mosaics adorning its walls and ceilings depicted religious iconography, creating an immersive environment that facilitated contemplation and worship. Moreover, the cathedral's central position within the imperial capital underscored its pivotal role in shaping the religious identity of the Byzantine people.
Beyond its religious significance, Hagia Sophia held immense political importance. It served as the ceremonial backdrop for imperial coronations, symbolizing the close relationship between the church and the state. The grandeur of the cathedral, with its towering dome and lavish ornamentation, reinforced the authority and prestige of the Byzantine rulers, projecting an image of opulence and power to both internal and external audiences.
Artistically, Hagia Sophia represented the pinnacle of Byzantine architectural and decorative achievement. Its innovative use of space, light, and architectural elements set new standards for monumental construction, inspiring generations of architects and artisans. The fusion of diverse cultural influences within its design reflected the empire's cosmopolitan ethos, embracing and synthesizing elements from Roman, Greek, and Eastern traditions to create a structure that transcended cultural boundaries.
Moreover, Hagia Sophia's enduring legacy in Byzantine culture is evident in its influence on artistic expression, religious symbolism, and the collective memory of the empire. Its architectural innovations and aesthetic splendor continue to captivate scholars and enthusiasts, offering a window into the artistic and cultural achievements of the Byzantine era.
In essence, the significance of Hagia Sophia in Byzantine culture cannot be overstated. It encapsulates the empire's religious devotion, political symbolism, and artistic brilliance, serving as a timeless testament to the multifaceted legacy of the Byzantine Empire.
The Legacy of Hagia Sophia in Modern Times
The legacy of Hagia Sophia transcends the boundaries of time, continuing to exert a profound influence on the modern world. As a testament to the enduring impact of the Byzantine Empire's cultural and architectural achievements, Hagia Sophia remains a revered symbol of artistic ingenuity and historical significance.
In the realm of architecture, Hagia Sophia's legacy endures as a source of inspiration for contemporary designers and architects. Its innovative structural design, characterized by the monumental dome and the strategic use of pendentives, continues to captivate the imagination of those seeking to push the boundaries of architectural innovation. The cathedral's seamless integration of diverse cultural influences serves as a compelling example of the power of synthesis and adaptation, resonating with modern efforts to create spaces that transcend cultural and geographical boundaries.
Furthermore, Hagia Sophia's impact extends beyond the realm of architecture, permeating the spheres of art, culture, and religious discourse. The cathedral's exquisite mosaics and ornate decorations have left an indelible mark on the artistic sensibilities of subsequent generations, inspiring a myriad of artistic expressions. Its influence on religious symbolism and iconography has endured, shaping the visual language of various religious traditions and artistic movements.
In the realm of cultural heritage, Hagia Sophia stands as a beacon of historical preservation and global significance. Its conversion into a museum in the 20th century further underscored its status as a symbol of cultural inclusivity and historical resonance. The preservation of Hagia Sophia as a UNESCO World Heritage Site serves as a testament to its universal value and its capacity to bridge diverse cultural narratives.
Moreover, the recent reversion of Hagia Sophia to a functioning mosque has reignited debates about the intersection of cultural heritage, religious identity, and global heritage management. This development has sparked discussions about the preservation of cultural landmarks and the complexities of navigating the intersection of history, religion, and contemporary societal values.
In essence, the legacy of Hagia Sophia in modern times is a multifaceted tapestry of architectural, artistic, and cultural influence. Its enduring resonance serves as a reminder of the timeless power of human creativity and the capacity of cultural landmarks to transcend the confines of history, inspiring and challenging contemporary societies to engage with their heritage in meaningful and inclusive ways.